Middle East Space Roundup: 7 to 13 May 2023
A summary of all the space news in the Greater Middle East over the past week, powered by AzurX

The following are the major space developments in the Greater Middle East region tracked by Middle East Space Monitor over the past week:
8 May 2023
In Israel WeSpace Technologies, a startup founded in 2019, plans to launch a small spacecraft called a "hopper" that can fly payloads over the lunar surface to collect data. The autonomous craft can navigate craters and rifts where constant radio communication is impossible and is designed to fly over obstacles. WeSpace hopes to contribute to the Artemis programme, providing mobility to meet NASA's Moon-to-Mars objectives, and sees a commercial market for its services once lunar mining infrastructure is in place. WeSpace's CEO, Yifat Feffer, believes the hoppers will provide the surface intelligence that mining companies will need.
Yahsat, the UAE’s premier satellite communications provider, has announced its Q1 2023 financial results, with year-on-year growth in revenue, EBITDA, and net income, which increased 2%, 4%, and 35%, respectively, during the quarter. The company also reported that its contracted future revenue of AED 7 billion ($1.9 billion), equivalent to 4.4 times last twelve-month revenue, highlights its strong position to continue driving future ambitions and delivering sustainable long-term growth. Yahsat's revenue reached AED 369 million ($100 million) for the first time in its history, driven by strong growth of 29% in managed solutions, and further growth in the infrastructure and data solutions businesses. Its EBITDA and net income surged by 8% and 46%, respectively, on a normalised basis. Yahsat has a robust balance sheet with negative net debt, strong cash position, and long-term visibility of future cash flows, which continues to support its investment in organic growth and opportunistic acquisitions without impacting its progressive dividend policy. The upcoming Thuraya-4 NGS satellite, due to be launched in 2024, followed by two potential new satellites, Al Yah 4 and Al Yah 5, reinforce Yahsat's direction and present unique growth opportunities.
Bahrain’s Minister of Industry and Commerce, Abdulla bin Adel Fakhro, leads a delegation of Bahraini trade officials and business leaders to Japan where they visited the headquarters of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Japan’s national space agency. The minister stresses the importance of space cooperation between Bahrain and Japan as a foundational contribution to building a diversified economy based on knowledge and innovation.
9 May 2023
Azerbaijan's state space corporation, Azercosmos, has signed a cooperation agreement with the U.S. company SpaceX, with the aim of launching new satellites into orbit. The Chairman of the Board of Azercosmos, Samaddin Asadov, revealed that Azerbaijani satellites would be launched using SpaceX's Falcon 9 launch vehicle. As part of the agreement, internet services based on Starlink, SpaceX's global satellite constellation for high-speed broadband internet access, will be provided in Azerbaijan. The cooperation is expected to improve internet coverage in the country, particularly in remote areas. Furthermore, SpaceX's participation in the International Astronautical Congress, to be held in Baku in October 2023, was also discussed.
Israel’s Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd., a global leader in satellite networking technology, solutions, and services, has released its first-quarter 2023 financial results, reporting $59.0 million in revenue, a 15% increase from the same period in 2022. GAAP operating income was $7.0 million, compared to a GAAP operating loss of $1.0 million in Q1 2022, while non-GAAP operating income was $5.3 million, compared to a non-GAAP operating loss of $0.3 million in Q1 2022. Gilat's net income was $5.6 million, or $0.10 earnings per diluted share, compared to a net loss of $2.5 million, or a loss of $0.04 per share, in Q1 2022. The company has also raised its GAAP operating income and adjusted EBITDA guidance, with a year-over-year growth of 81% and 31% at the midpoint, respectively. Gilat's CEO, Adi Sfadia, noted that the company is well-positioned, with strong revenue growth and backlog, to execute its growth strategy. Additionally, Gilat is acquiring DataPath Inc., a U.S. defence integrator, to enhance its defence offerings.
Details about the UAE's second interplanetary mission, which was announced in 2021, have been revealed in a conference paper to be presented in June 2023 at the Asteroids, Comets, Meteors Conference in Flagstaff, Arizona. The interplanetary mission will involve sending a spacecraft to the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The conference paper has revealed the seven asteroids the mission will visit. These are 10253 Westerwald, 623 Chimaera, 13294 Rockox, 88055, 23871, 59980, and 269 Justitia, with the spacecraft making a landing attempt on the last. To get there, it will require gravity assistance from Earth, Venus, and Mars. The primary objectives of the programme are resources, technologies, and fundamental science, while the mission's high-priority objectives are innovation, public engagement, and the development of space sector industrial infrastructure in the UAE. The as yet unnamed spacecraft will also use a solar electric propulsion system for flybys.
Italian news publication Nigrizia reports that five countries, including Algeria and Egypt, have ordered Russian military reconnaissance satellites. This marks a clear comeback for Russia in the military space reconnaissance industry, despite the decline of its space industry. The Algerian military budget has rapidly increased in 2023, and the country is expected to spend around $18 billion this year to strengthen its defence sector. The acquisition of military reconnaissance satellites could benefit the Algerian military, traditionally superior to that of its neighbour and rival Morocco. To correct the military imbalance between the two neighbouring countries, the collaboration of the Moroccan military with Israel is seen as a counterweight to Algeria. The Algerian decision to acquire Russian satellites has raised alarms among senior U.S. politicians, with Republican Senator Marco Rubio of Florida calling for sanctions under the Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
10 May 2023
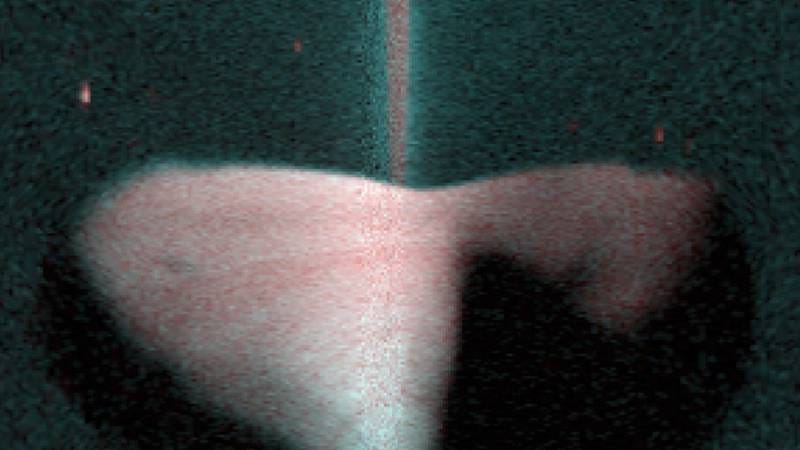
The UAE's Hope probe has captured a stunning nightside image of Mars's moon Deimos. The spacecraft has been studying the planet since February 2021, sending back data on the Red Planet's upper atmospheric conditions and space weather. In January, the spacecraft began its observations of the Red Planet and the smaller of its two moons. The latest image of Deimos shows the moon's nightside against the hydrogen glow in the sky. Last month, Hope sent back fascinating details of Deimos, challenging a long-standing theory that Mars’s moons are captured asteroids. Findings point to a planetary origin, meaning that the rock may have come from Mars itself.
11 May 2023
During a discussion of a new draft law on space activities at the meeting of Azerbaijan's Parliamentary Committee on Economic Policy, Industry, and Entrepreneurship, Chairman of the Board of Azercosmos state space corporation, Samaddin Asadov, announced that Azerbaijan plans to increase the number of its satellites in Earth orbit. Asadov stated that Azerbaijan aims to serve its national interests through space activities, as well as for commercial purposes. He also highlighted that all TV channels of Azerbaijan and Georgia broadcast via Azerbaijani satellites, and that Azerbaijan is not dependent on satellites of foreign countries. Asadov further added that Azerbaijan has started implementing new satellite projects, including the Azersky-2 Earth observation project together with companies from Israel, to include Israel Aerospace Industries. The first Earth observation satellite is expected to be launched in 2025 and the second in 2027. Both Azersky-2 satellites will replace the recently inoperable Azersky-1. Moreover, Malaysia will transfer its geostationary orbital position to Azerbaijan, and Azerbaijan will be able to launch four to six satellites, if needed. The Azercosmos space agency owns two communication satellites, Azerspace-1 and Azerspace-2.
Iran and Oman have allegedly agreed to collaborate in the space sector, as well as in data transit and postal services, according to official news agency IRNA. During a meeting between Iranian Minister of Information and Communications Technology Isa Zarepour and Omani Minister of Transport, Communications, and Information Technology Saeed bin Hamoud al-Maawali in Tehran, Zarepour expressed Iran's capability to build remote sensing and communications satellites for launch into low Earth orbits. The Omani minister highlighted the numerous areas for cooperation in communications and information technology and added that the national post companies of both countries signed a memorandum of understanding at the end of the meeting. Interestingly, media in Oman have not reported on this alleged space cooperation agreement, suggesting that Iran may have exaggerated the tenor of the discussions with their Omani counterparts.
12 May 2023
The UAE’s Etisalat by e& has launched its new Maritime SATCOMS portfolio of services to cater to the demands of the regional maritime industry in the UAE and beyond. The fully managed maritime service and equipment solution is compliant with local regulations and provides coverage for private yachts, commercial shipping, and oil barges of all sizes. The service offers a range of competitively priced, flexible bandwidth options featuring relatively higher committed information rates, round-the-clock support services, and a locally operated, fully managed service. The complete maritime information communications technology (ICT) solution suite includes managed internet, managed Wi-Fi, managed TV, internet of things (IoT), and other applications for crew welfare. This new offering by Etisalat by e& is new competition for the UAE’s other maritime satellite communications provider Thuraya, a subsidiary of Yahsat.
The UAE Space Agency participated in the UAE Climate Tech event as part of its commitment to promoting sustainability efforts and showcasing the latest projects and contributions in developing software and solutions to overcome national and global challenges. The UAE Space Agency announced the launch of phase two of the Space Analytics and Solutions (SAS) Programme to combat climate change, which includes three new challenges: the Air Quality challenge, the Infrastructure challenge, and the Losses and Damages challenge, aimed at offering entrepreneurs and researchers advisory and financial support to develop space applications to tackle climate change challenges. During the event, the UAE Space Agency also signed a memorandum of understanding with ADNOC, the UAE’s largest oil company, to collaborate on research and development of satellite technology in the energy sector, launching new joint projects, and utilising space applications to increase the work efficiency of public and private sectors. Participants were introduced to several initiatives in the fields of food security, greenhouse gases monitoring, environmental and vegetation monitoring, and infrastructure, as part of the Space Analytics and Solutions (SAS) Programme, and briefed on the Climate Change Challenge and the next phases of utilising satellite data to innovate new scalable solutions to support agricultural and environmental efforts and face the challenges of food security and climate change.
Recommended Reading
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS), a global think tank that is headquartered in London, and has an office in Manama, Bahrain, releases a report titled Watching Iran: The ISR Gulf. U.S. intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capacity in the Arab Gulf region, which is critical for monitoring Iran, is being drawn elsewhere due to greater demands in other regions such as Ukraine and the Asia-Pacific. The Gulf region's own capabilities are insufficient to replace the resources being redeployed, and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries are reluctant to cooperate on ISR. This has hampered the GCC's collective capacity to counter Tehran, which remains the Gulf states' primary security concern. The IISS paper explores the value of ISR as a contributor to regional deterrence and an essential element of armed forces' capacity in the event of war. It includes three chapters, which review Iran's military capabilities and the regional-security challenge it presents, demonstrate the value of ISR, and assess regional ISR capabilities, to include satellite reconnaissance, and options for bolstering them. While the demand for ISR to monitor Iran has not lessened, the U.S. is shifting its focus and leaving a gap in regional ISR capacity.

In Via Satellite, Robert Bell writes that access to safe drinking water is a rising concern for most of the world. About one in four people do not have access to safe drinking water, and half of the world's population experiences severe water scarcity for part of the year. This leads to food scarcity because producing one person's daily food requires between 2,000 and 5,000 litres of water. Water scarcity and flooding are rising challenges. Experts predict that future wars will be fought over access to water, as water conflicts have been happening since at least 2500 BC. However, satellite technology provides a better path, as demonstrated by Egypt and Ethiopia's dispute over the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam. Ursa Space Systems generated satellite intelligence using synthetic aperture radar (SAR) to measure changes in the size of the Ethiopian dam's reservoir over time. This helped Ethiopia prove it was managing water flows without endangering Egypt or other downstream countries, allowing the two nations to resolve their differences.
Be sure to catch up with space activities in the region in the next edition of Middle East Space Monitor’s space roundup!

